Our process model
Our procedure model organizes the project process into different phases. Each of these phases is associated with appropriate methods.
Rigid and bureaucratic models of action are not suitable for successfully completing today’s projects under guarantee. Combining traditional methods with modern approaches is the right approach for the targeted solution of complex tasks.
In this article we would like to briefly present our procedure model. This gives you an idea of how we approach projects. If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Table of Contents

Prozessoptimierung für SAP – SMART Prozess
Process model – Why?
Projects must be successfully implemented in terms of quality, deadline and cost. For this purpose, process models are used to control and structure projects. Complex tasks are carried out according to standardized, well-known and proven methods of procedure.
Due to the differences in nature and scope of projects, a uniform, rigid approach model cannot be used. In general, a subdivision of the procedure models into agile and general models can be made.
At munich enterprise software, we meet new, complex and dynamic projects with an agile approach. This places particular emphasis on the factor “human” and its interpersonal relationships.
In order to achieve sustainable effectiveness and efficiency, our procedure model is adapted to the customer-specific project situation.
Tailoring is the key to success here. This includes:
- Joint planning of the process phases
- Coordinated selection of appropriate methods
- Compliant scheduling
- Ensuring communication as the basis for project success
- Distribution of load, responsibility and knowledge among the entire team
munich enterprise software uses the procedure model to:
- Always ensure the same processes
- Avoid mistakes in advance
- To benefit from the experience of the past years
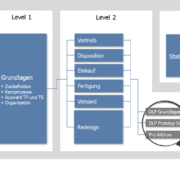
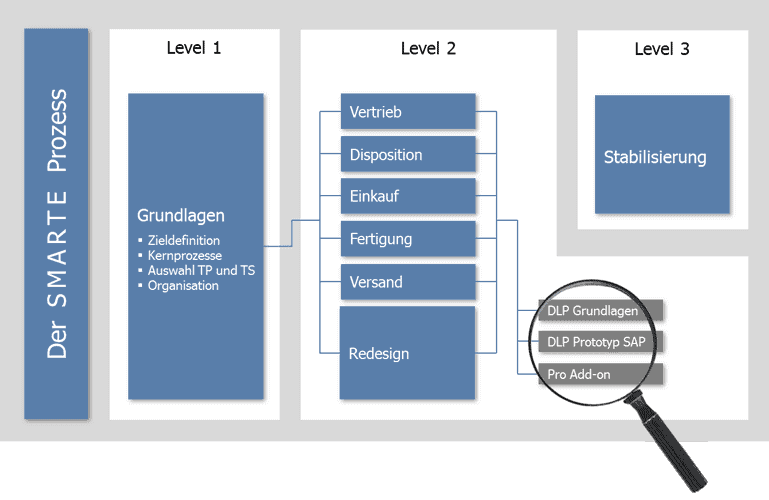
The 6 phases of the process model
Our procedure model is divided into 6phases, which are accompanied by 5 workstreams:
- Initialization: vote on the idea of the project; agreement that a project should be set up; Target definition; Defining the project framework
- Analysis: recording and analysis of requirements; Description of the process sequences
- Design: Definition of the solution
- Realization: Implementation of the solution
- Test: Verification and test of the realized solution; Consideration of the interplay
- Application: Productive setting
The 5 Workstreams
A holistic view of different workstreams guarantees project success. Workstreams define workspaces that are edited by a specific team. As part of the m/e/s procedure model, the following 5Workstreams are distinguished:
- Project Management: Cross-phase workstream that provides the entire
the life cycle of the project and ensures the success of the project - Process and organisation: recording and defining processes, setting up the relevant organisation
- Application: Tasks and objectives for analysis, design, implementation and testing
- Infrastructure: Deploy the appropriate infrastructure to support the Application workstream across all phases
- Training & Support: Overarching support, creation and communication of training materials
Methods and tools
Methods: Observation, Structured Interviews, Questionnaire, SWOT, Benchmark, ABC Analysis, CPM, Value Stream Analysis, Cost-Benefit Analysis, Lean Production, SCOR, SCRUM, Feedback, Creative Methods such as Brainstorming, Brainwriting, 6-3-5
Tools: SAP-PS, MS Project, Visio, MS Office, Mindmap
Types
munich enterprise software distinguishes between the following types of projects:
- IT project
- Process Optimization Project
The difference between IT and process optimization projects is as follows:
- Aim (formulation)
- Measurability
- Iterative approach
- Fokus