Terms and techniques from SAP archiving
Overview of terms SAP archiving
SAP archiving includes a variety of terms that are important for understanding and implementing this process. Overview of the most important terms:
- Archiving: The process of storing data and documents outside the SAP database in a long-term available format.
- Archive object: A logical unit of data that is archived, such as receipts, purchase orders, or invoices.
- Archive file: The saved file that contains the archived data and is placed in an archive store.
- Indexing: The process of creating search and access indexes on archived data to enable fast searching.
- Data deletion: The process of removing obsolete or no longer needed data from the SAP database after successful archiving.
- ArchiveLink: An interface that enables the linking of documents in external content management systems with SAP objects.
- Information Lifecycle Management (ILM): The management of data throughout its lifecycle, including archiving, storage, and deletion.
- SAP Content Server: A stand-alone server that serves as a central repository for documents and files outside the database.
- Data Retention: The definition of data retention periods to meet legal and business requirements.
- Data consistency: Ensuring data integrity and consistency between the SAP database and the archived data in the archive store.
What is SAP ArchivLink?
SAP ArchivLink is an interface that makes it possible to store and access documents and information from SAP applications in external content management systems (CMS) or archive stores. This relieves the SAP databases and manages and archives documents more efficiently. The use of ArchivLink enables seamless integration of documents into SAP business processes and provides features such as indexing, versioning, and access control for secure and effective document management.
Table of Contents

What is SAP KPRO?
SAP KPRO stands for “Knowledge Service Provider” and is a module in SAP that enables context-sensitive management of documents and files. With KPRO, documents, such as technical drawings, contracts, or images, are stored in external content management systems (CMS) and linked to SAP objects. The link is made by the context, e.g. customer number or order number, which enables an efficient search and display of relevant documents within the SAP applications. KPRO also offers workflow functions for controlling document processes and versioning for document management.
SAP Content Server (Content Management Server)
The SAP Content Server is a stand-alone server that stores documents and files outside the database. The documents are linked to the corresponding SAP data records via the SAP Content Server, which serves as a central repository for files and thus relieves the database.
SAP Archive Development Kit (ADK)
The SAP Archive Development Kit (ADK) makes it possible to archive data and documents directly on the SAP application server. This allows flexible, application-specific archiving and is particularly useful when specific requirements are not covered by standard archiving solutions.
SAP Document Management System (DMS)
The SAP Document Management System (DMS) offers advanced functions for the management of documents and technical drawings. It enables the integration of documents into SAP business processes, including versioning, status management, and workflow support.
SAP Information Lifecycle Management (ILM)
ILM is a comprehensive approach to managing the entire lifecycle of information and data in an organization. It enables efficient and rule-based management of data, including archiving, deletion, backup, and access control.
Old and New World – Example Order
In ECC with message processing – processing of the message and storage of the document via the ArchivLink interface via the communication service Content Management Service can be stored on the content server.
In S4 without message processing – This uses the outmanagement framework. However, the outmanagement no longer has an interface to ArchivLink.
ArchivLink is still “state of the art” in S4. In the future, however, this standard will become less and less important. In the cloud, only the SAP-independent CMIS standard is relevant. There is no longer an ArchivLink. This also eliminates the barcode scenarios of ArchivLink.
What is CMIS?
CMIS stands for “Content Management Interoperability Services” and is a standard protocol developed by the Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards (OASIS). CMIS enables interaction between different content management systems (CMS) and content repositories, regardless of their manufacturer. The goal is to provide a unified interface through which applications can access and manage documents and content.
With CMIS, external content management systems and document repositories are seamlessly integrated into SAP applications. Documents and content are retrieved, created, modified and deleted via standardized CMIS interfaces. This facilitates the integration of non-SAP systems. Heterogeneous content management solutions can be combined with SAP software.
Some of the benefits of CMIS include:
Interoperability: CMIS enables different content management systems to work together, regardless of their manufacturer, which simplifies integration and data exchange.
Reusability: Since CMIS is a standardized interface, applications and integration solutions can be developed that can work with any CMS system that supports CMIS.
Access control: CMIS supports security and access control for documents and content. This ensures the confidentiality and integrity of information.
Versioning: The CMIS interface also supports the management of versions of documents, which is important when changes to files and content need to be tracked.
Easy integration: The use of CMIS simplifies the integration of external content management systems into SAP applications and enables efficient use of information across different systems.
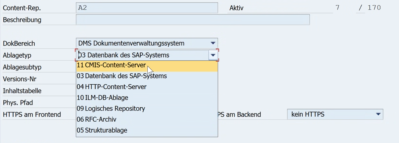
SAP CMIS Adapter in Transaction OAC0
Overall, it is important to note that not all SAP applications automatically support CMIS. The use of CMIS may require specific configurations or enhancements to enable communication between SAP and CMS systems. Therefore, companies considering such an integration should take advantage of SAP documentation and, if necessary, consulting support to understand the steps and opportunities required.
SAP will support the CMIS standard as a SICF service in Netweaver. There is no need to switch from the non-CMIS-capable content server with S4. The ArchivLink standard is also still supported with S4.
Is there a new technique for archiving with SAP – successor ArchivLink?
Currently, there is no direct successor to SAP ArchivLink as a new technology for archiving with SAP. SAP ArchivLink is still one of the main methods for integrating external content management systems (CMS) and archive stores with SAP systems.
But SAP is always evolving, and perhaps there will soon be new ways to secure data. SAP is constantly releasing new updates and versions to better respond to customer needs and provide new solutions.
We recommend that you check the official SAP information from time to time. This will keep you up to date on possible innovations. Perhaps in the future there will be new functions at SAP that improve or complement the ArchivLink.
Further key points:
- Enterprise Content Management Integration (ECMI)
- API – API_CV_ATTACHMENT_SRV
- 3220119 – Business applications in SAP S/4HANA that have adopted Harmonized Document Management (HDM)




